Great Lakes Food Webs: Impact of Invasive Species on Lake Huron Food Web
By Erica Sprague
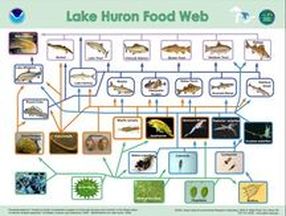
Click on image to download a printable version of this lesson plan
We would greatly appreciate your feedback! Click here to complete a short survey telling us about your experience with this lesson plan.
By Erica Sprague
Click on image to download a printable version of this lesson plan
We would greatly appreciate your feedback! Click here to complete a short survey telling us about your experience with this lesson plan.
Lesson Overview
This lesson is integrated into a project about biodiversity. Students have learned about the different energy roles in food webs and why biodiversity is vital to the survival of an ecosystem. This lesson focuses on the effect of invasive species in the Lake Huron Food Web. They will identify the invaders as producers, consumers, decomposers or scavengers and investigate how the food web could potentially change as a result of the invasive species.
Sources Consulted
Lake Huron Food Web (NOAA GLERL) https://www.glerl.noaa.gov/pubs/brochures/foodweb/LHfoodweb.pdf
All other Lake Food Webs
Learning Objectives
After the lesson, students will be able to…
Michigan Science Standards Addressed
SEP: Science and Engineering Practices
List of Materials
Room Arrangement or Special Needs
New Vocabulary
1. Non-Native Species: A species that not indigenous to the ecosystem in which it currently lives and may have been introduced to an area by human means. A non-native species is not always considered an invasive species.
2. Invasive Species: A non-native species in an ecosystem that may cause harm to the economy, the environment or human health.
3. Producer: an organism in a food web whose role it is to make their own food using energy from the sun; producers are often food sources for 1st level consumers; producers can be plants and some photosynthetic algae.
4. Consumer: an organism in a food web whose role it is to eat other living things; 1st level consumers eat producers, 2nd level consumers eat 1st level, etc.
5. Detrivore: organism that feeds upon detritus
6. Omnivore: organism that feeds upon both plant and animal food sources
7. Herbivore: organism that feeds primarily upon plant food sources
8. Carnivore: organism that feeds primarily upon animal food sources, includes piscivores, which are specifically fish that feed on other fish.
9. Forage: to search widely for food resources
10. Macroinvertebrates: invertebrate (no backbone)organisms that can be captured
11. Zooplankton: small animal plankton and larval stages of larger animals
12. Phytoplankton: microscopic plant/photosynthetic plankton
5E Model Lesson Plan
Engage/Guiding Question: What are the organisms currently living in the Lake Huron Food Web that are non native and/or invasive and what effect do they have on the native organisms?
Students have already had a lesson on what an ecosystem is and how food webs exist within ecosystems. You may take an additional lesson before studying the Lake Huron Food web to study and review the vocabulary. Ask students why new species that are introduced into a food web can’t just “get along” with the others. What makes one newly introduced species non native, and another one invasive? How does the introduction of a non native species have the potential to affect not just one or a few native species, but take down the entire food web and reestablish a new one?
Explore/Activities
Explain/Lab Data and Evidence
Elaborate/Student Share Out
Evaluate/Apply Knowledge
This lesson is integrated into a project about biodiversity. Students have learned about the different energy roles in food webs and why biodiversity is vital to the survival of an ecosystem. This lesson focuses on the effect of invasive species in the Lake Huron Food Web. They will identify the invaders as producers, consumers, decomposers or scavengers and investigate how the food web could potentially change as a result of the invasive species.
Sources Consulted
Lake Huron Food Web (NOAA GLERL) https://www.glerl.noaa.gov/pubs/brochures/foodweb/LHfoodweb.pdf
All other Lake Food Webs
Learning Objectives
After the lesson, students will be able to…
- Identify organisms within a food web that are decomposers, producers and different level consumers
- Predict changes in a food web if organisms are added or removed
Michigan Science Standards Addressed
SEP: Science and Engineering Practices
- Analyzing and Interpreting Data
- MS-LS2-1 Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem.
- MS-LS2-3 Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy among living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem.
- MS-LS2-4 Construct an argument supported by empirical evidence that changes to physical or biological components of an ecosystem affect populations.
- Cause and Effect
- Systems and System Models
List of Materials
- Copy of Great Lakes Food Web (I used Lake Huron for this lesson, others are available). Laminated copies can be used multiple years and kids can write on them with washable markers to help identify the different parts of the food web.
Room Arrangement or Special Needs
- Students are grouped together for the activities and lab (3-4 students max)
New Vocabulary
1. Non-Native Species: A species that not indigenous to the ecosystem in which it currently lives and may have been introduced to an area by human means. A non-native species is not always considered an invasive species.
2. Invasive Species: A non-native species in an ecosystem that may cause harm to the economy, the environment or human health.
3. Producer: an organism in a food web whose role it is to make their own food using energy from the sun; producers are often food sources for 1st level consumers; producers can be plants and some photosynthetic algae.
4. Consumer: an organism in a food web whose role it is to eat other living things; 1st level consumers eat producers, 2nd level consumers eat 1st level, etc.
5. Detrivore: organism that feeds upon detritus
6. Omnivore: organism that feeds upon both plant and animal food sources
7. Herbivore: organism that feeds primarily upon plant food sources
8. Carnivore: organism that feeds primarily upon animal food sources, includes piscivores, which are specifically fish that feed on other fish.
9. Forage: to search widely for food resources
10. Macroinvertebrates: invertebrate (no backbone)organisms that can be captured
11. Zooplankton: small animal plankton and larval stages of larger animals
12. Phytoplankton: microscopic plant/photosynthetic plankton
5E Model Lesson Plan
Engage/Guiding Question: What are the organisms currently living in the Lake Huron Food Web that are non native and/or invasive and what effect do they have on the native organisms?
Students have already had a lesson on what an ecosystem is and how food webs exist within ecosystems. You may take an additional lesson before studying the Lake Huron Food web to study and review the vocabulary. Ask students why new species that are introduced into a food web can’t just “get along” with the others. What makes one newly introduced species non native, and another one invasive? How does the introduction of a non native species have the potential to affect not just one or a few native species, but take down the entire food web and reestablish a new one?
Explore/Activities
- Review all vocabulary before starting the lesson. Students may need several examples or pictures to understand macroinvertebrates, zooplankton and phytoplankton.
- Jigsaw Reading: Use page 2 of the Lake Huron Food Web PDF and assign small groups a different section of the reading. Cut out the sections and give only one section to a group at a time. Students will read about the different groups of the food web and try to identify non native and invasive species. Allow time for groups to meet and share what they have learned until all groups have met with other groups.
- If time/money allows, students can have an engaging experience that is tailored to this activity by participating in the BaySail Science Under Sail. Click the link to learn more about this experience. Many scholarships and grants are available for Mid-Michigan schools to make this a possibility.
Explain/Lab Data and Evidence
- Use a laminated copy of the Lake Huron Food Web and give groups of students a dry erase marker to help them sort and organize each creature on the food web in the worksheet for decomposers, producers, 1st level consumers, 2nd level consumer, etc Lake Huron Food Web Worksheet
- Students can use different colored markers for each role
- Students can mark P, 1, 2, 3 or D next to each organism
- Or, you can use a paper version for students to write on.
- Students will also need to make a special notation next to any organism that is considered non native (NN) or an invasive species (IS). We will use this information during elaborate/student share out.
Elaborate/Student Share Out
- Using a class copy or on the board, have students compile a list of organisms for each role. Sharing out will allow students to consider adding or changing the group list. It should also alert students that some organisms fall into multiple roles.
- Dig deeper into the Lake Huron Food web after all non native and invasive species have been identified and discuss:
- Discussion 1: Name a first level consumer that is considered NN or IS. Students will probably bring up the Zebra or Quagga mussel. Ask students what the mussels eat. Have groups of students look at the food web and discuss which other organisms eat the same food. Ask the class which organisms would be most affected if the mussel at all the food.
- Discussion 2: What level consumer is the sea lamprey? What eats a sea lamprey? Other than the fish it preys on, what other organisms in the food web are indirectly affected by the lamprey? If nothing eats the lamprey, how to you think people are trying to control the spread and damage of lamprey?
Evaluate/Apply Knowledge
- Option 1: Apply knowledge to one of the other Great Lakes Food Webs and ask similar questions for an assessment. Teachers could develop another chart or multiple choice quiz geared towards looking at an analyzing another food web.
- Option 2: Students can design a solution for getting rid of one invasive species currently in the Great Lakes. This could be an extension to the lesson to incorporate engineering standards to evaluate competing design solutions.
- Option 3: Teachers can design a writing prompt and assign a writing assessment to ask students to describe how all parts of the food web can be affected by a single non native or invasive

New lesson plan ideas are welcome and will be uploaded as they are received and approved.
Instructions for submitting lesson plans for:
About invasive species,
About science and science careers
For information about submitting new lesson plans, please contact jchadde(at)mtu.edu
Lesson plan ideas from other web sites:
From Pennsylvania Sea Grant: 10 lesson plans about interactions of invasive species, biodiversity, and climate change
Creation of the above page of educational resources was funded in part by the Michigan Invasive Species Grant Program through the Departments of Natural Resources, Environmental Quality, and Agricultural and Rural Development.
This material is also based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1614187.
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.